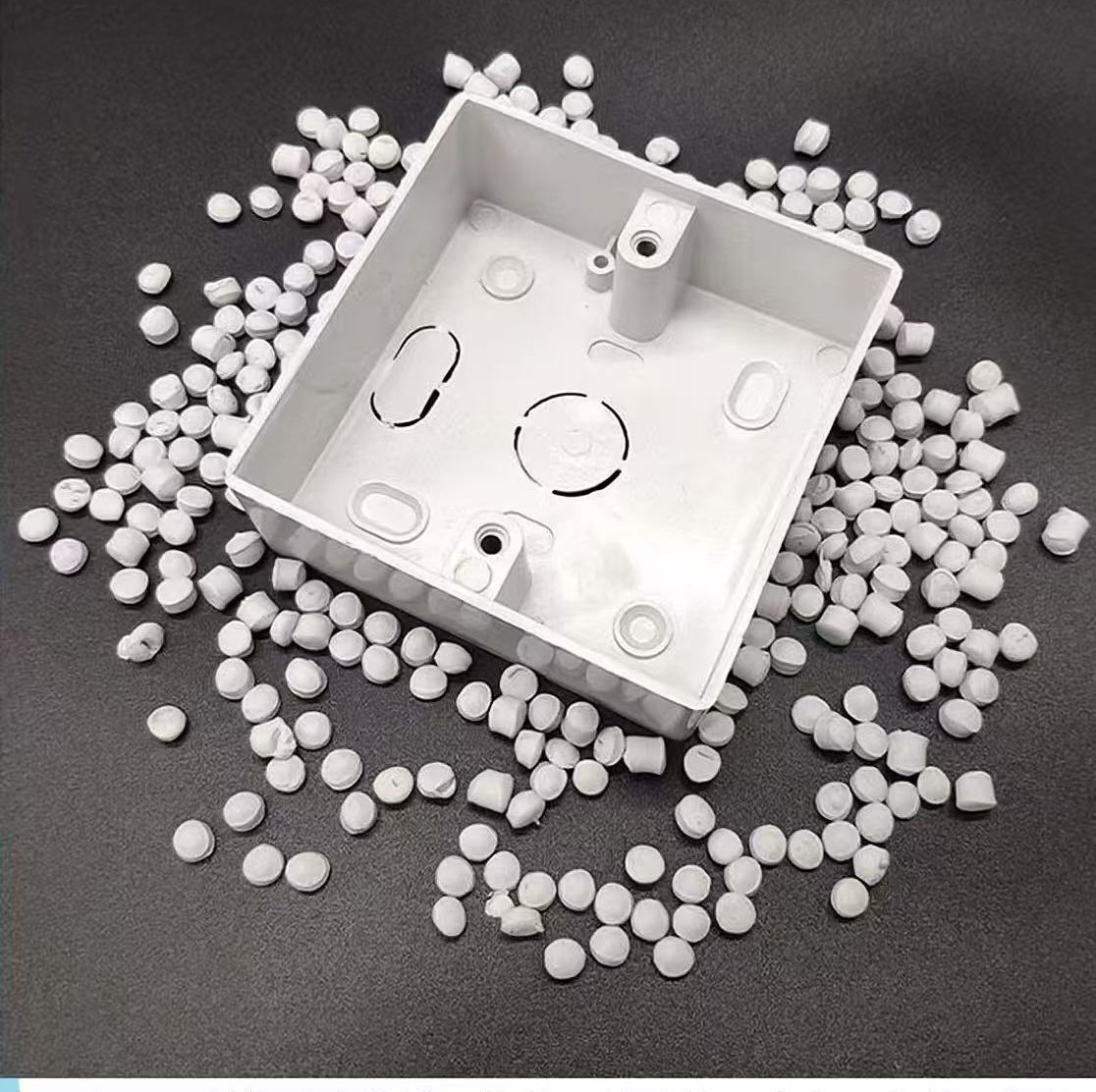
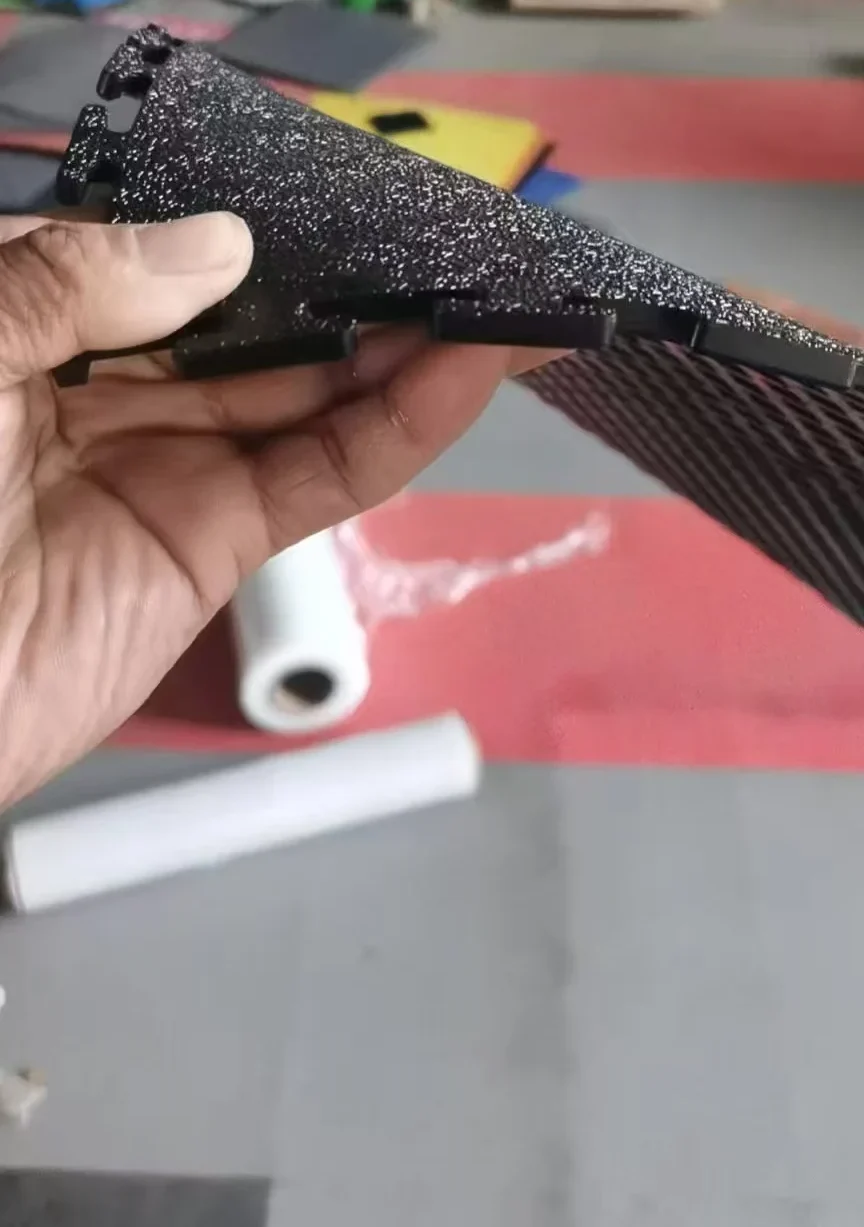
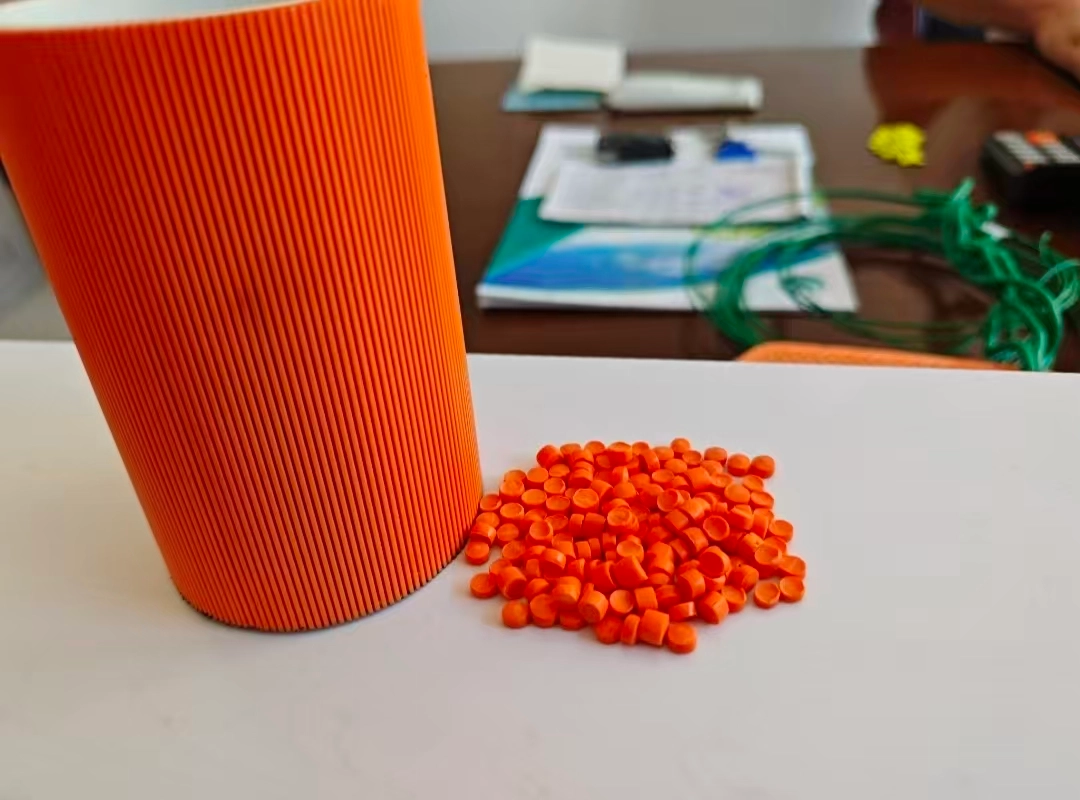
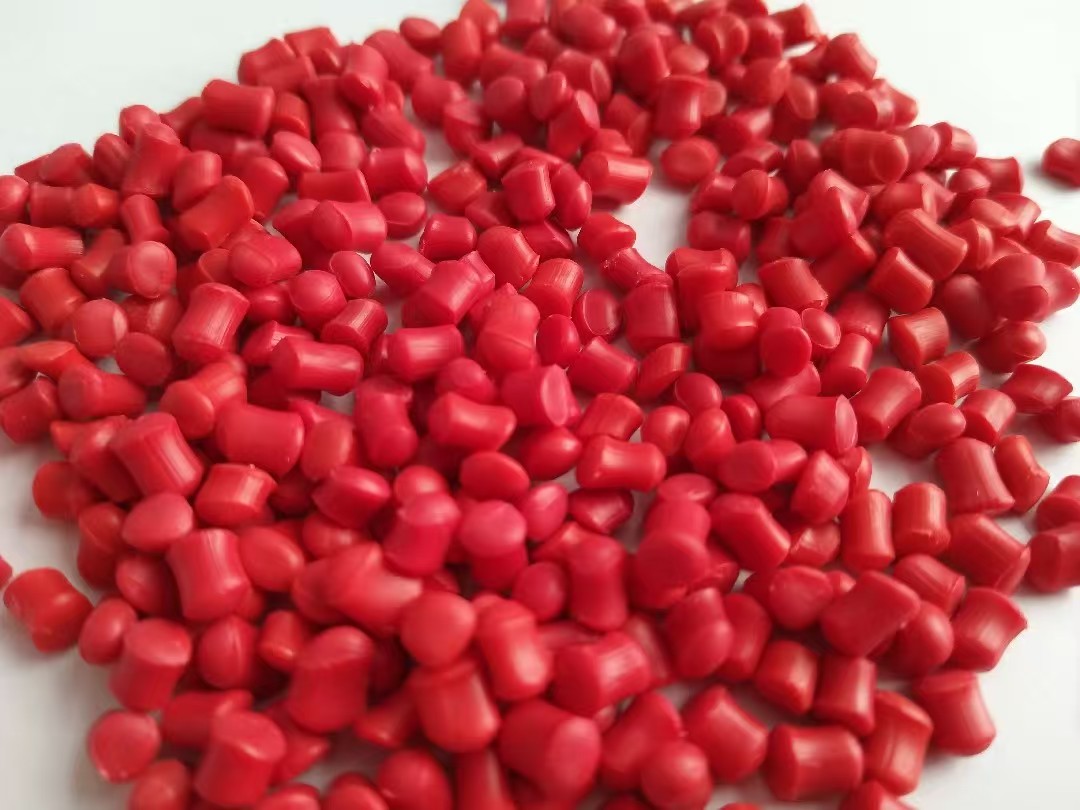
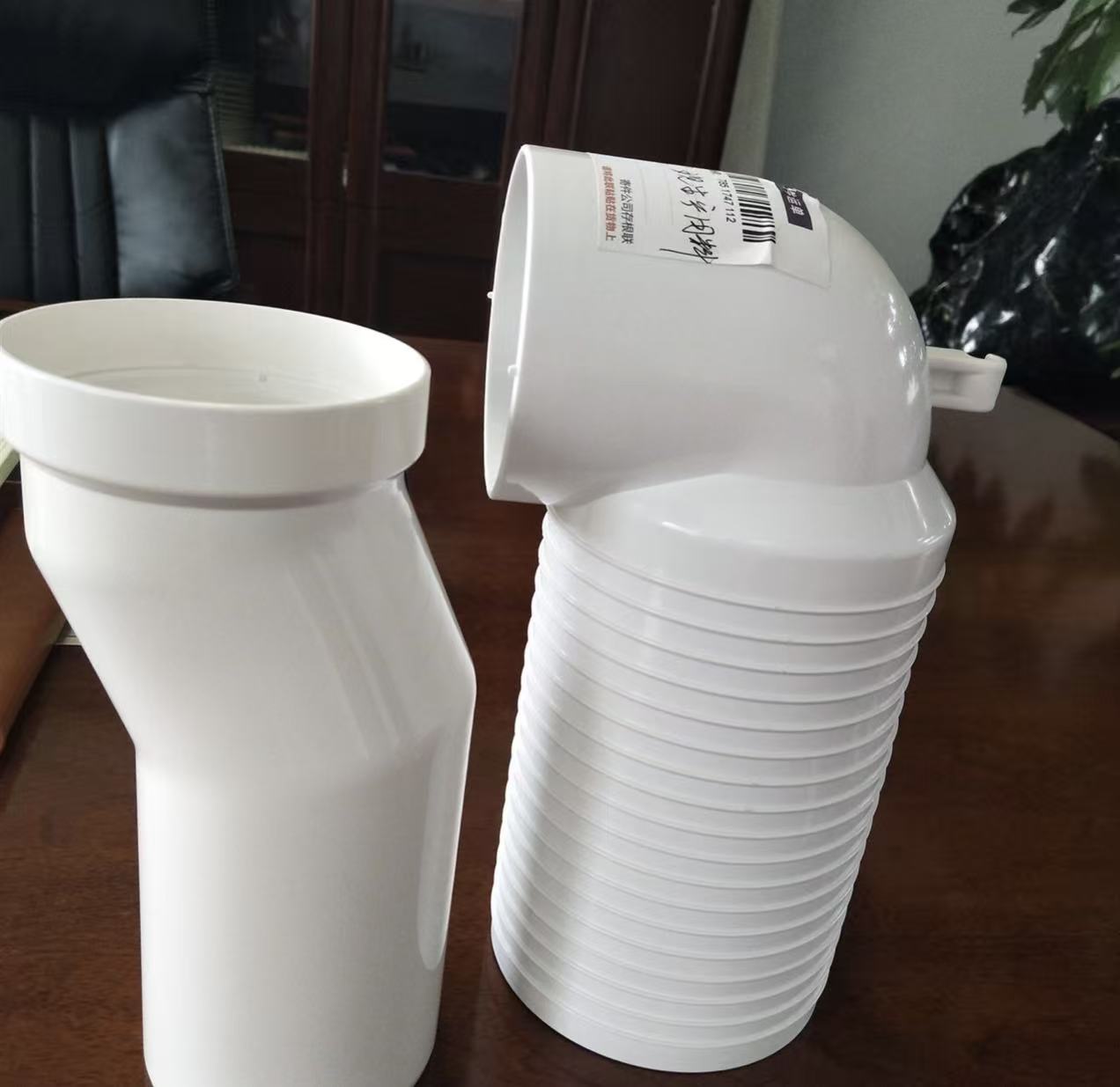
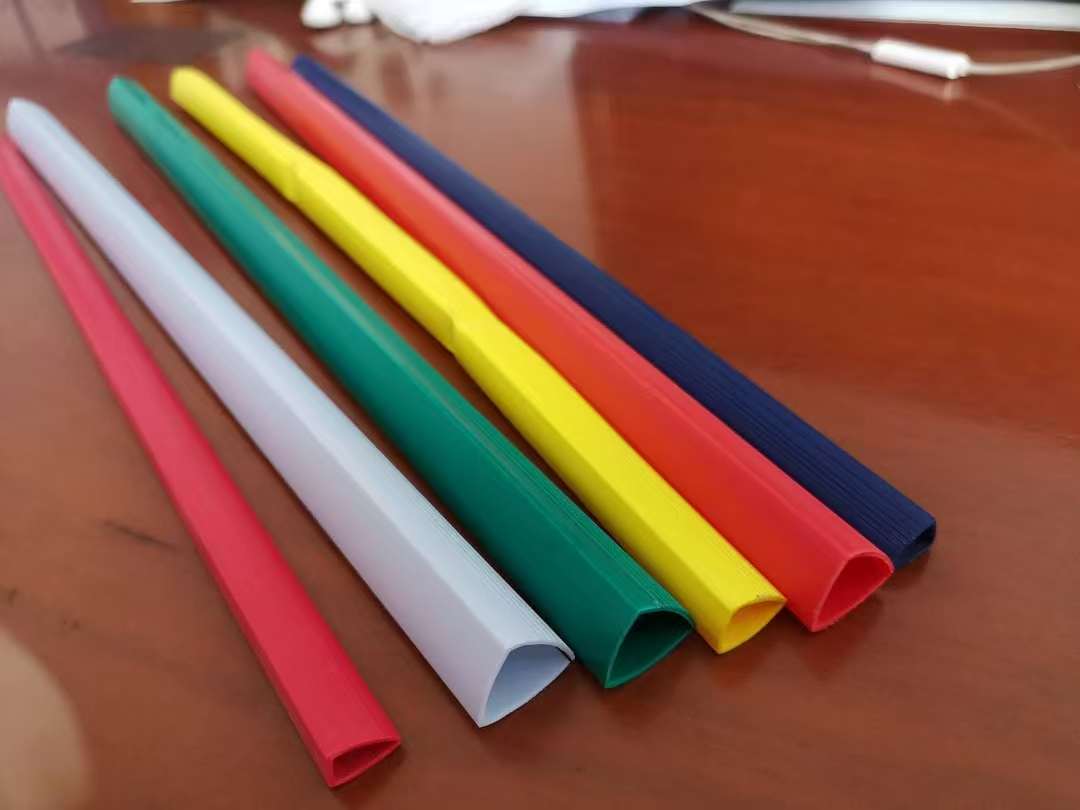
For injection molding electrical accessories like lamp holders, sockets, and power strips, PVC granules must be formulated to meet strict safety, durability, and performance standards. These components require a balance of excellent electrical insulation, flame retardancy, heat resistance, and mechanical strength.
Key Formulation & Performance Requirements
The formulation for these accessories focuses on several non-negotiable safety and performance features:
-
Flame Retardancy & Self-Extinguishing: Electrical components carry a risk of sparking or overheating. The PVC compound must have a high flame-retardant rating (typically UL94 V-0) to prevent the spread of fire, a critical safety standard for consumer and industrial electrical goods.
-
Superior Electrical Insulation: The primary function is to safely insulate live electrical contacts. This requires high volume resistivity and dielectric strength to prevent current leakage or short circuits.
-
Heat Resistance & Thermal Stability: Components must not deform or degrade under the heat generated by electrical currents or from ambient conditions. A high Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT) and good long-term thermal aging resistance are essential.
-
Impact Strength & Durability: Sockets and plugs experience physical insertion and removal forces. The material needs good impact resistance (especially at lower temperatures) and tensile strength to withstand daily mechanical stress without cracking.
-
Safe & Compliant Formulation: Modern regulations demand the elimination of hazardous substances. This involves using heavy-metal-free stabilizers (like Calcium-Zinc systems instead of lead-based ones) and ensuring the compound is RoHS and REACH compliant.