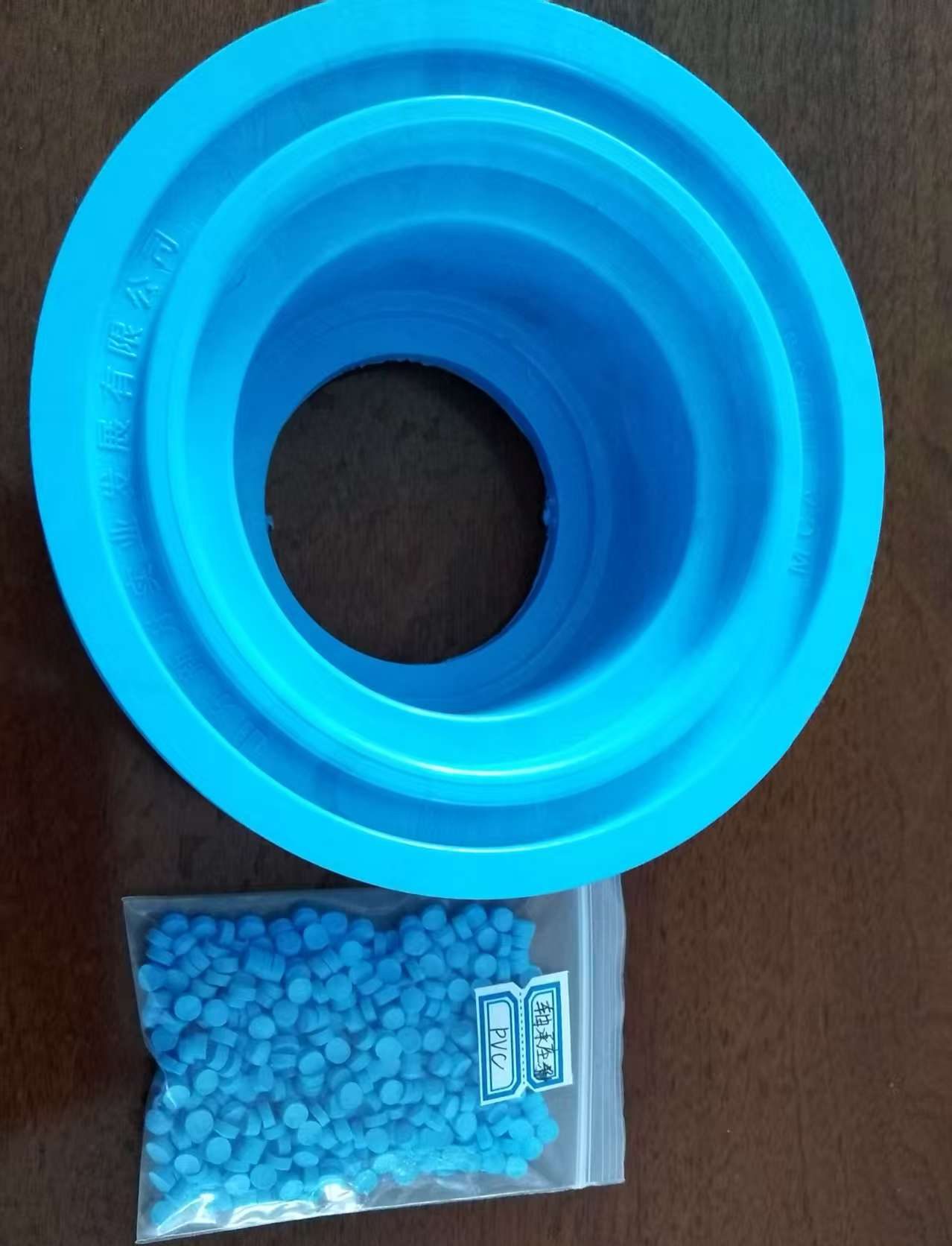
Engineering Superior Performance: PVC Granules for Bearing Carriers
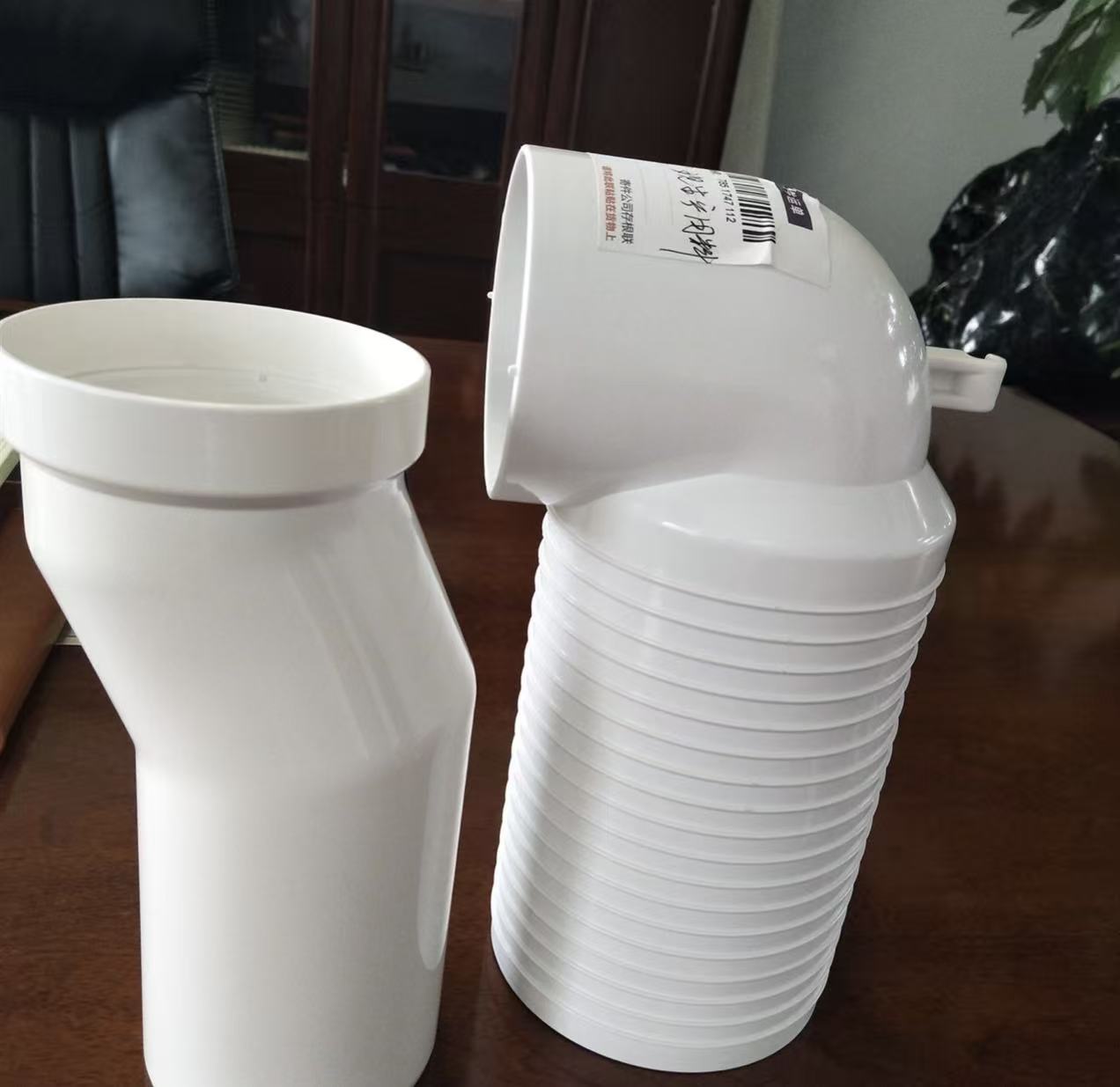
In the world of mechanical components, the bearing carrier plays a critical, often understated role. It is the steadfast housing that maintains precise alignment, supports loads, and ensures the smooth rotation of bearings in everything from industrial conveyors to agricultural machinery. While metals have been the traditional choice, advanced Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) formulations are emerging as a superior alternative, offering a compelling blend of durability, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. This article delves into the formulation of specialized PVC granules engineered to meet the rigorous demands of high-performance bearing carriers.
The Formulation Strategy: Balancing Strength, Stability, and Wear
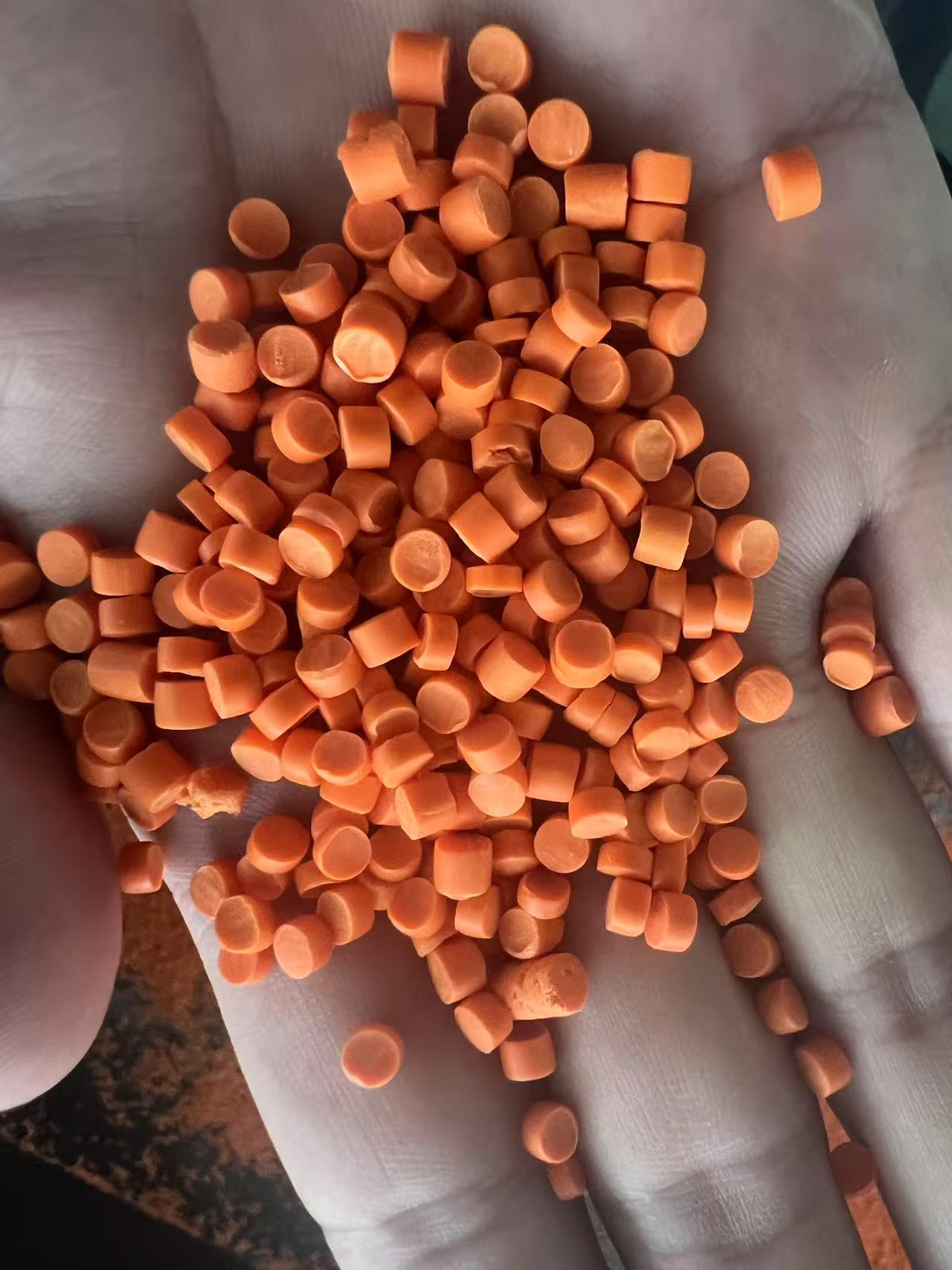
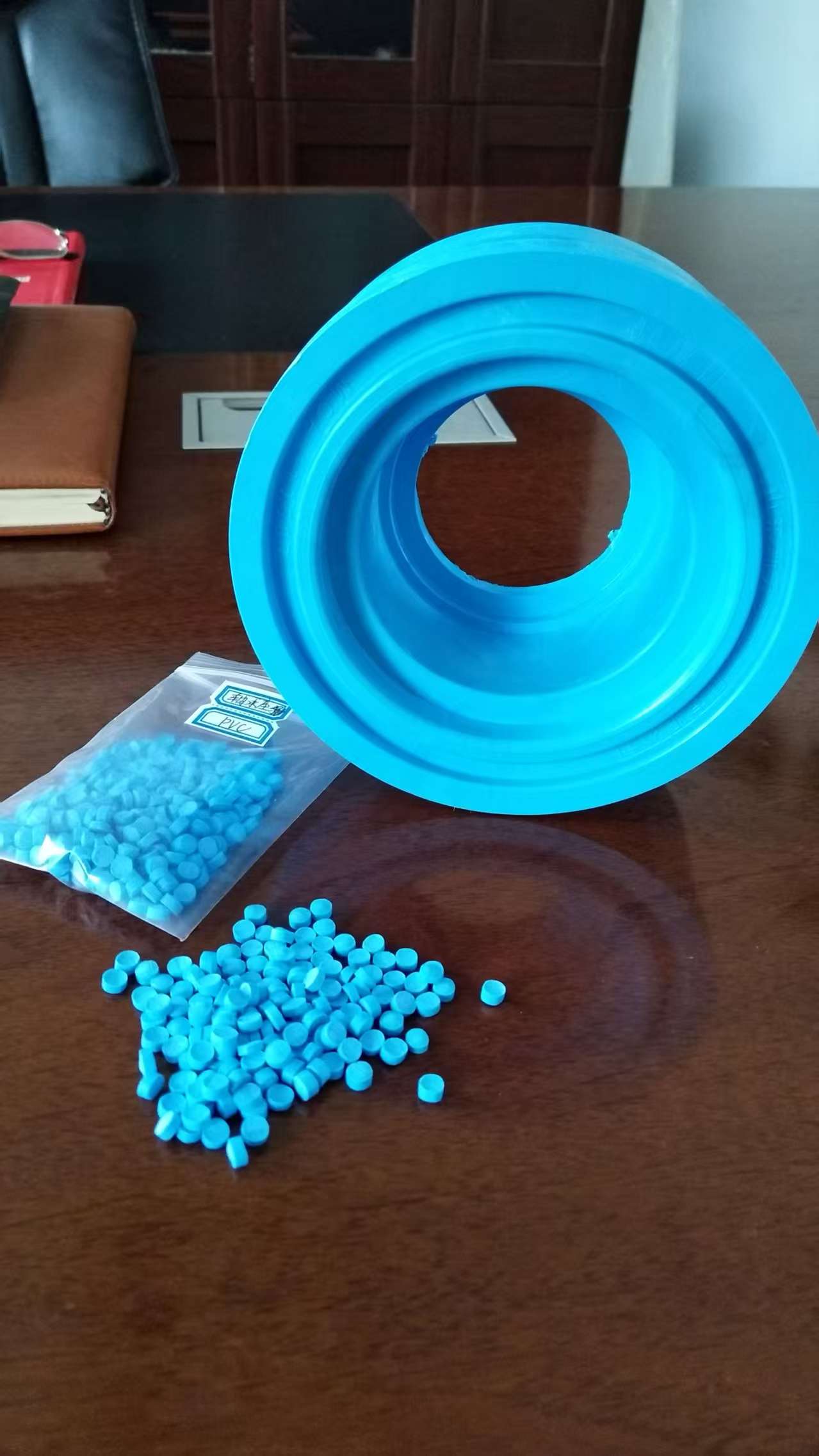
Creating PVC granules for bearing carriers is not about using a standard compound; it is an exercise in precision engineering. The formulation must address several simultaneous challenges: resisting constant mechanical stress, maintaining dimensional stability under load and temperature variation, and enduring wear over extended operational lifetimes. The core recipe revolves around a rigid PVC-U (Unplasticized) base, chosen for its inherent strength and stiffness. To this base, a synergistic system of additives is integrated.
Key additives include high-performance impact modifiers, such as Acrylic-based (ACR) or Chlorinated Polyethylene (CPE), which are crucial for absorbing shock and preventing brittle fracture under sudden or uneven loading. The stabilization system, typically based on advanced Calcium-Zinc (CaZn) complexes, is paramount for ensuring long-term thermal stability during processing and in service, preventing degradation that could compromise integrity. Furthermore, internal lubricants like specialized waxes are carefully balanced to ensure excellent melt flow for molding complex carrier geometries while enhancing the final product’s surface finish to reduce friction. For applications requiring extra resistance to abrasion and wear—a common demand in bearing housings—specific wear-resistant additives can be incorporated into the matrix.
Conclusion: A Partner for Precision
Transitioning to or selecting PVC for bearing carriers is a decision driven by the pursuit of reliability, longevity, and total cost efficiency. A generic PVC compound will not suffice; success hinges on a purpose-built formulation that transforms base resin into a high-performance engineering material. By partnering with a compounder that masters the science of impact modification, stabilization, and tribology, manufacturers can produce bearing carriers that excel in harsh environments—resisting corrosion, dampening vibration, and outperforming traditional materials. The future of mechanical components lies in such advanced polymer solutions, where tailored PVC granules provide the foundation for innovation and durability.